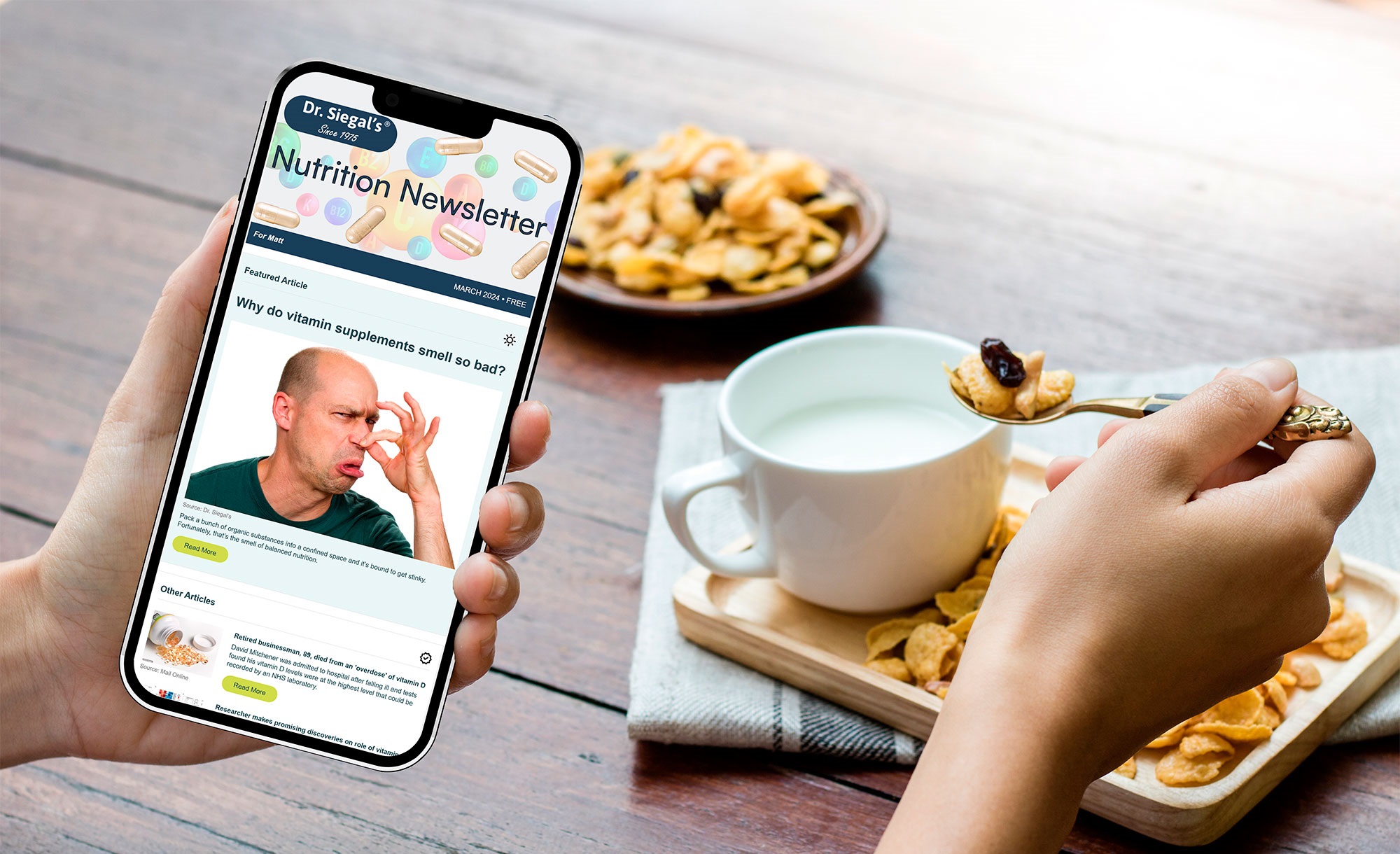
What is It?*
Source Type: Water-soluble vitamin
Source(s):
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for various biological processes in the body. Vitamin B12 is used as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, as well as the metabolism of proteins and fats. We also need vitamin B12 for proper red blood cell formation, cell metabolism, and nerve function.
Benefits*
Vitamin B12 is essential for producing red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body. Vitamin B12 is also beneficial for maintaining cardiovascular health and cognitive function.
Effectiveness*
Vitamin B12 supplements are highly effective in the prevention and treatment of B12 deficiency-related conditions, such as megaloblastic or pernicious anemia.
Vitamin B12 is involved in the breakdown of homocysteine, which is a protein that is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events and cognitive decline. But, even though research has shown that vitamin B12 is effective for reducing homocysteine levels, this has not directly translated to reduced rates of cognitive decline or cardiovascular events. More research is still needed.
Risks*
There is currently no upper limit set for vitamin B12, as there is a lack of evidence of toxicity at high exposures. Vitamin B12 has the potential to interact with certain medications, such as gastric acid inhibitors and Metformin. These medications can reduce the absorption of vitamin B12 and lead to vitamin B12 deficiency.